Introduction
Managing team collaboration and data security is critical in modern analytics. Power BI Workspaces offer an efficient way for teams to build, share, and manage reports and dashboards. Microsoft Power BI introduces 4 workspace roles – Admin, Member, Contributor, and Viewer – each with specific capabilities to ensure smooth operations.
In this article, we’ll explore these roles, their permissions, and why assigning the right roles is essential for secure and productive teamwork.
What is a Power BI Workspace?
A workspace in Power BI is a shared environment where users collaborate to create, share, and manage content such as dashboards, reports, and datasets.
Imagine a team building an interactive sales report:
- Designers create visuals,
- Analysts modify datasets, and
- Executives view insights.
Power BI workspace roles ensure that each user has the right permissions to perform their tasks effectively.
The 4 Power BI Workspace Roles
- Admin
- Member
- Contributor
- Viewer
Admin
Who is this for?
Ideal for project managers or team leads who require full control over the workspace.
Capabilities:
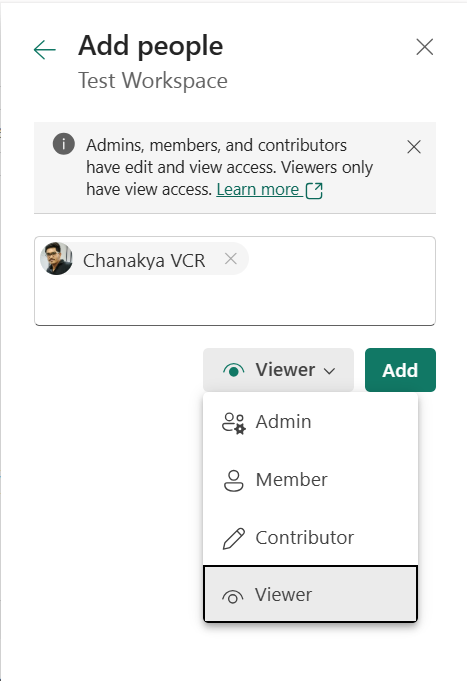
- Add, remove, or manage user roles.
- Update and delete the workspace.
- Manage data refresh schedules and gateway connections.
- Assign semantic model permissions.
- Feature dashboards on colleagues’ homepages.
Use Case:
A project owner overseeing multiple teams managing sensitive datasets.
Member
Who is this for?
Team members are actively involved in creating, sharing, and updating content.
Capabilities:
- Publish, create, edit, and delete reports.
- Share reports via apps.
- Update apps and refresh data.
- Modify gateway connections.
Use Case:
An analyst creating dashboards and updating apps for stakeholders.
Contributor
Who is this for?
Content creators focused on developing and refining dashboards without managing settings.
Capabilities:
- Create and edit content like reports and visuals.
- Interact with dataflows and semantic models.
- Copy reports to develop goals.
Limitations:
- Cannot share reports or update apps.
Use Case:
A junior analyst creating visuals while leaving app updates to senior team members.
Viewer
Who is this for?
Stakeholders or consumers who only need to interact with finalized reports.
Capabilities:
- View and interact with published content.
- Subscribe to reports for automatic updates.
- Analyse data via Excel exports.
Limitations:
- Cannot edit, manage, or share content.
Use Case:
Executives reviewing high-level performance dashboards.
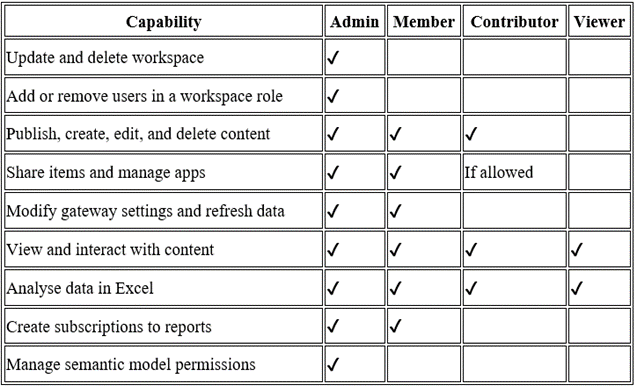
Comparing Power BI Workspace Roles
To highlight role differences, here’s a quick comparison table:
Admin
Who is this for?
Ideal for project managers or team leads who require full control over the workspace.
Capabilities:
- Add, remove, or manage user roles.
- Update and delete the workspace.
- Manage data refresh schedules and gateway connections.
- Assign semantic model permissions.
- Feature dashboards on colleagues’ homepages.
Use Case:
A project owner overseeing multiple teams managing sensitive datasets.
Member
Who is this for?
Team members are actively involved in creating, sharing, and updating content.
Capabilities:
- Publish, create, edit, and delete reports.
- Share reports via apps.
- Update apps and refresh data.
- Modify gateway connections.
Use Case:
An analyst creating dashboards and updating apps for stakeholders.
Contributor
Who is this for?
Content creators focused on developing and refining dashboards without managing settings.
Capabilities:
- Create and edit content like reports and visuals.
- Interact with dataflows and semantic models.
- Copy reports to develop goals.
Limitations:
- Cannot share reports or update apps.
Use Case:
A junior analyst creating visuals while leaving app updates to senior team members.
Viewer
Who is this for?
Stakeholders or consumers who only need to interact with finalized reports.
Capabilities:
- View and interact with published content.
- Subscribe to reports for automatic updates.
- Analyse data via Excel exports.
Limitations:
- Cannot edit, manage, or share content.
Use Case:
Executives reviewing high-level performance dashboards.
Comparing Power BI Workspace Roles
To highlight role differences, here’s a quick comparison table:
Why Assigning Roles Matters
Assigning the right roles in Power BI ensures:
- Security: Only authorized users can modify or share sensitive data.
- Productivity: Roles clearly define responsibilities, avoiding workflow confusion.
- Collaboration: Different team members contribute based on their expertise.
For example, a Viewer consumes reports for insights, while a Contributor builds and refines dashboards for stakeholders.
Practical Use Case
Let’s say a company’s sales team is creating a performance report:
- Admin: The team lead manages access, ensuring the workspace remains secure.
- Members: Analysts publish and update dashboards for stakeholders.
- Contributors: Junior analysts add visuals or adjust data models.
- Viewers: Executives access the final dashboards to make decisions.
Conclusion
Understanding Power BI workspace roles Admin, Member, Contributor, and Viewer is key to managing user permissions effectively. By assigning roles strategically, teams can collaborate seamlessly, maintain data security, and deliver impactful reports to stakeholders.
Whether you’re managing a large analytics project or sharing reports with stakeholders, using Power BI roles ensures everyone has the access they need without compromising control.