In today’s fast-moving world, every sector—from finance and manufacturing to pharma—depends on data for decision-making and innovation. Yet much of that data remains locked in separate systems, clouds, or partner environments. This fragmentation doesn’t just complicate IT—it slows down insights, innovation, and regulatory compliance.
With the Databricks Lakehouse Platform—and its features like Lakehouse Federation and Delta Sharing—you can break down silos, unify disparate data estates, and gain a full view of your business assets
This guide will demystify these two essential technologies, helping you understand when and how to use them—individually and together—to build a unified, secure, and agile data mesh.
Databricks Lakehouse Federation: Querying Data In Place
Databricks Lakehouse Federation is a query federation platform that lets you run queries against multiple external data sources directly from within your Databricks environment. The key here is that you can do this without the need to ingest or replicate the data. It’s based on the principle of data virtualization, allowing you to analyze data right where it lives.
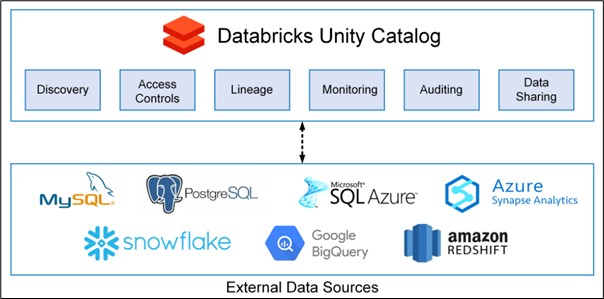
How It Works (Unity Catalog at the Core)
The central piece of Lakehouse Federation is Databricks Unity Catalog, which acts as a centralized metadata store and governance backbone. To enable federation, you configure two key securable objects within Unity Catalog:
- Connections: These objects store the path and credentials for accessing an external database system, such as a transactional database or a data warehouse.
- Foreign Catalogs: These objects mirror a database from an external system, allowing you to perform read-only queries on that data directly within your Databricks workspace.
When to Use Lakehouse Federation
Lakehouse Federation is ideal when you need to access live data without moving it into Databricks. Key use cases include:
- Ad-hoc Reporting and Proof-of-Concept Work: Quickly combine data from various sources for exploratory analysis or to validate new reports without setting up complex ETL pipelines.
- Accessing Operational Data: Query data directly from transactional databases (like MySQL, PostgreSQL) or data warehouses (like Snowflake, Amazon Redshift) without duplicating it.
- Minimizing Data Movement: This is crucial for use cases where you need to avoid data ingestion costs and latency, or where data must remain in its original system due to compliance or operational requirements.
- Incremental Migrations: Support workloads during phased migrations to Unity Catalog by creating a hybrid model where some data remains external while other data is managed by Unity Catalog.
- Internal Data Sharing: Provide a unified point of access to various internal data silos for different business units within your organization.
Benefits of Lakehouse Federation
- Simplified Data Workflows: Analysts and data scientists can access data from across your entire data estate using a single interface.
- Cost Efficiency: It helps you avoid the costs associated with data ingestion, storage, and duplication.
- Real-time Insights: Queries run directly on live data sources, ensuring your insights are always fresh.
- Consistent Governance: You can extend Unity Catalog’s robust security and governance to all external data sources.
Delta Sharing: Securely Sharing Data Beyond Boundaries
Delta Sharing is an open protocol developed by Databricks for securely sharing data with other organizations, regardless of the computing platforms they use. It allows data providers to share live data and AI assets—including tables, views, volumes, notebooks, and AI models—from their Unity Catalog-enabled Databricks workspaces with external recipients.
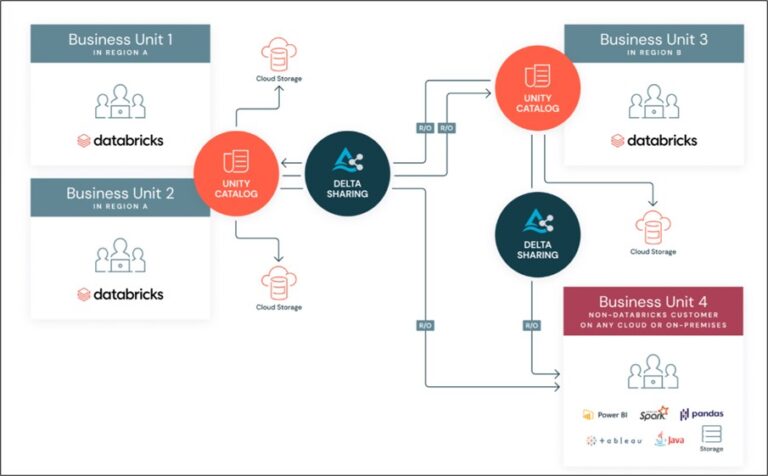
How It Works
Delta Sharing facilitates secure data exchange through “shares,” which are read-only collections of data assets. There are two primary ways to share data using Delta Sharing:
- Databricks-to-Databricks Sharing: This is used when both the provider and recipient have Unity Catalog-enabled Databricks workspaces. This method uses the built-in Delta Sharing server and offers enhanced features like notebook and AI model sharing, as well as Unity Catalog’s full governance, auditing, and usage tracking.
- Databricks Open Sharing Protocol: This allows providers with Unity Catalog-enabled workspaces to share tabular data with users on any computing platform. Recipients can use open-source Delta Sharing connectors for popular tools like Power BI, pandas, and open-source Spark.
When to Use Delta Sharing
- External Data Collaboration: Sharing data with business partners, customers, or suppliers for joint analysis, reporting, or product development.
- Cross-Organization/Cross-Cloud Sharing: Facilitating secure data exchange between different organizations, across various cloud providers, or between different geographic regions.
- Data Monetization: Creating new revenue streams by licensing or providing access to curated data products, often facilitated through platforms like the Databricks Marketplace.
- Internal Data Sharing Across Metastores: Securely sharing data between different Unity Catalog metastores within the same organization, which is particularly useful for large enterprises with distributed data teams or multi-cloud strategies.
Benefits of Delta Sharing
- Open Standard: It avoids vendor lock-in and enables broad interoperability.
- Secure and Governed: It integrates natively with Unity Catalog for centralized management, access control, and auditing of shared data.
- No Data Duplication (for Provider): Providers share a single live copy of the data, which minimizes storage costs and ensures data freshness.
- Flexibility: It supports sharing various data assets beyond just tables, and recipients can use their preferred tools to access the data.
Lakehouse Federation vs. Delta Sharing: Choosing the Right Tool
While both technologies tackle data accessibility, their core purposes are different.
Feature | Databricks Lakehouse Federation | Delta Sharing |
Primary Use Case | Internal, live querying of disparate data sources without ingestion. | External (or cross-metastore internal) sharing of data products with other organizations. |
Data Movement | No data movement; queries run against the source system. | No data copy by the provider; provides access to shared data. |
Data Access Type | Live, federated query access to operational and analytical data. | Secure, read-only access to curated data products. |
Target Audience | Internal data analysts, data scientists, and engineers. | External partners, customers, or internal teams across organizational boundaries. |
Underlying Data | Queries against existing tables in external databases (e.g., MySQL, Snowflake). | Shares Delta tables, views, volumes, notebooks, and AI models. |
Compute Location | Queries use both Databricks and the remote compute of the external system. | The recipient uses their own computing platform to read the shared data. |
Essentially, Lakehouse Federation is for internal data virtualization and unified access, while Delta Sharing is for secure data distribution and collaboration with external parties or across distinct organizational boundaries.
Performance and Security: A Deeper Look
Performance Considerations
Both technologies are designed with performance in mind, but they achieve it in different ways.
Lakehouse Federation performance depends heavily on the external data source and network efficiency. Databricks boosts this by using the Photon engine to push down filters and aggregations, cutting data transfer and offloading compute. For frequently used queries, materialized views can cache results and reduce latency. You can also tune JDBC parameters like fetchSize to speed up data retrieval.
Delta Sharing delivers fast, secure, and live data distribution by sharing a single copy of the data with no duplication overhead. Recipients read data through short-lived, pre-signed URLs that pull directly from the provider’s cloud storage, making large transfers efficient. For lower latency, recipients can create local cached copies or replica tables.
Security Considerations
Unity Catalog is the foundational security layer for both technologies.
For Lakehouse Federation –
- Security focuses on controlling internal access to external data sources.
- Credentials are centrally managed in Unity Catalog, eliminating the need for individual users to store or handle them.
- Unity Catalog’s fine-grained access controls (row and column level) apply to federated tables, so you can define granular permissions directly from Databricks
- All operations are auditable through detailed audit logs and lineage tracking
- Lakehouse Federation allows read-only queries, protecting operational data from accidental changes.
For Delta Sharing –
- It’s designed for secure data exchange, even across external organizations and platforms.
- Despite being an open protocol, it enforces strong security with end-to-end TLS encryption and short-lived credentials.
- When paired with Unity Catalog, you get centralized governance, unified access control, and full audit logging.
- Providers can set fine-grained permissions on shares to control exactly what recipients can access.
- For external sharing, Databricks lets you manage recipient tokens with options to set expiration, rotate them, or revoke access instantly.
Best Practices and Conclusion
To get the most out of these technologies, remember:
- Unity Catalog is Essential: Ensure your Databricks workspaces are Unity Catalog-enabled, as it is the foundational layer for managing everything.
- Optimize Performance: For Lakehouse Federation, monitor your external data sources and use materialized views for frequent queries. For Delta Sharing, be mindful of network latency and advise recipients on caching strategies if needed.
- Manage Costs: Be aware of potential data egress costs with Delta Sharing for cross-cloud transfers. For Lakehouse Federation, consider the compute costs on both Databricks and the remote system.
- Prioritize Security: Leverage Unity Catalog’s fine-grained access controls and regularly audit permissions for both federated and shared data.
- Promote Data Discovery: Use Unity Catalog’s tagging and commenting features to ensure all data assets are easily discoverable and understood.
Databricks Lakehouse Federation and Delta Sharing offer clear, practical paths to a unified and secure data landscape. By understanding their distinct strengths and using them in tandem, powered by the centralized governance of Unity Catalog, you can break down data silos, accelerate time to insight, and build a robust, scalable data mesh that unlocks the full potential of your organization’s data, no matter where it resides.
