The landscape of web development is constantly evolving. One of the most exciting shifts in recent years is the rise of serverless architecture—a model that frees developers from managing infrastructure. Whether you’re building a static site, a full-stack app, or an API-driven service, serverless web apps offer speed, scalability, and simplicity like never before.
But what exactly does “serverless” mean? Is it truly serverless? And how do you actually build and deploy one?
What Are Serverless Web Apps?
Contrary to the name, “serverless” doesn’t mean there are no servers. It means developers don’t need to manage or provision the servers themselves. The cloud provider (like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud) handles the infrastructure, allowing developers to focus purely on code.
Key Concepts:
- Backend as a Service (BaaS): Pre-built services like Firebase Auth, Firebase store, or AWS Cognito.
- Function as a Service (FaaS): Small functions triggered by events. Example: AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions.
- API Gateways: Manage HTTP requests and route them to serverless functions.
Why Choose Serverless?
- Here’s why teams and companies are adopting serverless:
- Faster Development: You don’t have to set up and maintain servers. Just write code and deploy.
- Cost-Effective: Pay only for what you use. If your function is idle, you’re not charged.
- Scalability by Default: Serverless functions automatically scale to handle more traffic.
- Security & Updates: Providers handle OS updates, patches, and runtime security.
- Simplified Architecture: Use microservices, edge computing, or JAM stack principles with ease.
How to Build a Serverless Web App:
Let’s walk through the steps with an example using Next.js + AWS Lambda + DynamoDB.
- Frontend: Static or React-Based UI
- Use Next.js or React to build the frontend.
- Host on Vercel, Netlify, or S3 + CloudFront for global delivery.
- Backend Logic: Serverless Functions
- Use AWS Lambda for your API logic.
- Deploy with Serverless Framework, Amplify, or AWS SAM.
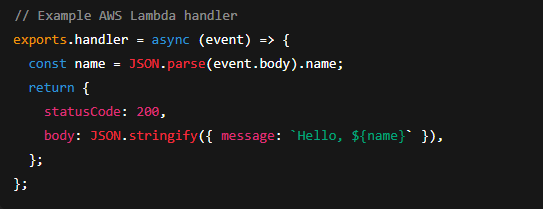
- Database: NoSQL or Serverless DB
- Choose Amazon DynamoDB, Firebase Firestore, or FaunaDB.
- These scales automatically and require no maintenance.
- Auth & Security
- Use Firebase Authentication, Auth0, or AWS Cognito.
- Secure APIs with JWT or OAuth tokens.
- Deploy and Monitor
- Use Serverless Framework: serverless deploy
- Set up logs, alerts, and error tracking using CloudWatch or Sentry.
Real-World Example: Event Booking App
Scenario:
You’re building an event booking app. You want it to:
- Load fast
- Scale during ticket launches
- Have low hosting costs
Solution:
- Frontend: React hosted on Vercel
- APIs: Serverless functions (e.g., create Booking, cancel Booking)
- Database: DynamoDB
- Auth: AWS Cognito
- Payments: Stripe webhook integrated with a Lambda
You now have an app that auto-scales, costs little during off-season, and has global latency improvements.
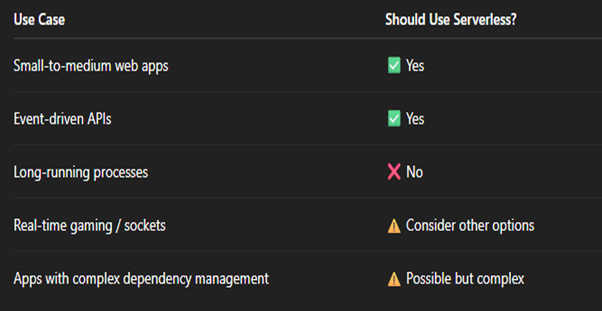
When Not to Use Serverless?
Conclusion: Empowering the Future with Serverless
Serverless architecture is more than just a trend — it’s a paradigm shift in how we build modern web applications. By removing the burden of infrastructure management, serverless allows teams to focus on what truly matters: delivering features, improving user experience, and innovating faster.
Whether you’re a solo developer prototyping a side project or an enterprise scaling globally, serverless offers:
- Agility to deploy features quickly
- Cost-efficiency by paying only for usage
- Resilience through automatic scaling and fault tolerance
- Simplicity by reducing DevOps overhead
As cloud platforms evolve, serverless is becoming even more powerful with support for edge computing, AI integration, and hybrid models.
In short, serverless democratizes software development, enabling anyone with an idea to build scalable, secure, and performant apps — without needing a fleet of servers or a team of sysadmins.
So next time you start a project, ask not “How do I host this?”, but rather “Can I go serverless and scale effortlessly?”
-Kabin M
FullStack Developer
Step 7: Verify the Migration
After the migration is complete, connect to your s3and verify that the database, tables, data, stored procedures, triggers, and events have been successfully migrated.
Step 8: (Optional) Delete DMS Resources
- Delete the DMS replication instance
- Remove the endpoints
- Retain or archive the S3 data as per your retention policy
- To prevent additional costs
Conclusion
Migrating from Amazon RDS to Amazon S3 with AWS DMS is a strategic and high-impact move toward building a modern, scalable, and analytics-ready data platform. With its ability to deliver near-zero downtime, continuous data replication, and cost-efficient storage, AWS DMS empowers you to accelerate digital transformation with confidence.
Unlock the full potential of your data infrastructure—kickstart your AWS DMS migration today and drive intelligent, data-driven outcomes!
